Understanding Decentralized Exchanges

What is a DEX?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) enable transactions directly between crypto traders in a peer-to-peer marketplace. There is no central authority that ensures that both parties carry out a trade correctly. Instead, there is a smart contract that executes a trade if both parties agree to the exchange. If one of the two parties behaves improperly, the smart contract will not be executed and will return the initial funds.
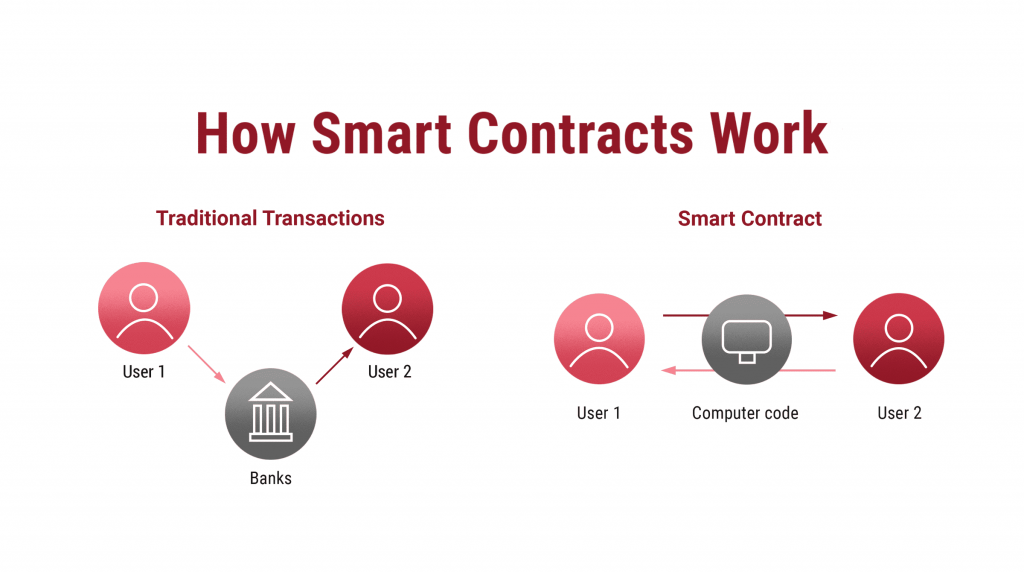
What differentiates DEXs from any other exchange?
Decentralized exchanges were created to align with Bitcoin’s fundamental purpose as a decentralized and anonymous currency.
DEXs have been key in the development of today’s crypto ecosystem, serving as an open-source space where traders can exchange their coins anonymously. For many people, having to exchange their tokens in centralized exchanges carried risks they were unwilling to take, such as providing detailed personal information to centralized exchanges and leaving privacy in the hands of third parties.

Open-source protocols, like DEXs, are game-changing for users. Everyone can access a DEX and see all exchanges and updates. The protocol’s underlying code is also public. When an open-source protocol is widely used, more and more qualified people review its code. This helps mitigate the risk of a bad actor trying to cheat or steal from the DEX, as users would be able to easily see and report such abuse publicly.
Before 2020, Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) were widely used in crypto. It was not until the development and popularization of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) in mid-2020 that DEXs grew popular. Unlike DEXs, CEXs are not open-source, and many faced a range of issues that DEXs are unlikely to deal with — from freezing users’ funds to money laundering to directly stealing their clients’ funds stored in the exchange.
DEXs also provide several advantages to traders, the three most notable being anonymity, token availability, and reduced security risk.
- Anonymity: To interact with DEXs and exchange your coins, you only need to connect your wallet; no personal data or account creation is required.
- Token availability: As long as a token is on the blockchain and has liquidity, it can be traded on DEXs. On the other hand, to trade on a CEX, tokens have to go through a tedious selection process to be listed on the exchange.
- Security risk: As DEXs have no custody of your funds, you should be insulated if the exchange is somehow hacked.
How DEXs work
The majority of decentralized exchanges use two methods of exchange: the order book method (the same method used by the US stock market) and the automated market maker (the most widely-used method). With the order book method, the buyer/seller hands their money to the smart contract. When someone who wants to perform the same trade you offer is found, the order is executed and the swap is made. The problem with this method is that it may take significant time before a buyer/seller accepts the trade.
The automated market maker is the backbone of modern DEXs. Instead of trading with another user, you trade with a liquidity pool. This liquidity pool is formed by different users who deposit their coins into the pool in exchange for a commission.
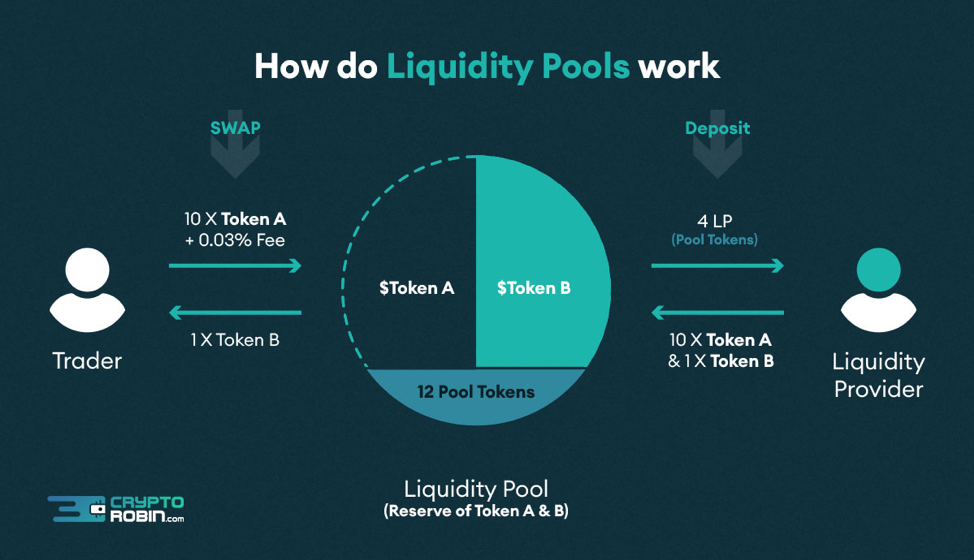
The DEX with the highest volume in 2021 was Uniswap, the most popular decentralized exchange on the Ethereum blockchain. During 2021, Uniswap earned around $1.1 billion in fees, and trading volume surpassed $1 trillion!
Clearly, DEXs provide significant value for users, offering a wide variety of tokens to traders and providing passive commissions to liquidity providers. DEXs offer a significant value proposition, and their use is expected to increase sharply in the coming years.












